Future Generali India Life Insurance Company Limited is now Generali Central Life Insurance Company Limited. Generali Central Life Insurance Company Limited – A joint venture between Generali – one of the world’s leading insurers and Central Bank of India, India’s finest nationalised bank.
Future Generali India Life Insurance Company Limited is now Generali Central Life Insurance Company Limited. Generali Central Life Insurance Company Limited – A joint venture between Generali – one of the world’s leading insurers and Central Bank of India, India’s finest nationalised bank.
Tax on Dividend Income in India Rules and Exemption Guide
 8 mins
8 mins 55.8K
55.8KMany of you are wondering whether dividends received are taxed in your hands because they are considered income.
Let us now examine the taxation of dividend income in further depth.
What is Dividend?
The term "dividend" usually refers to the distribution of the profit earned by the company to its shareholders (investors). However, as per Section 2(22) of the Income Tax Act, the dividend must also include the following:
- Accumulated (collected) profits are distributed to shareholders, that requires the company's assets to be distributed;
- Out of the company's accumulated (collected) profits, debentures or deposit certificates are distributed to shareholders, and bonus shares are issued to preference shareholders;
- On the company's liquidation, a distribution of accrued (collected) profits are distributed to the stockholders;
- Accumulated (collected) profits from the company's capital reductions are distributed to shareholders;
- A loan or advance given to a shareholder by a closely held company out of its accumulated profits.
Sources of Dividend
Dividends are available from the following sources:
- Domestic company – whose shares you own
- Foreign company – whose shares you have purchased
- Equity mutual funds – if you choose to receive dividends
- Debt fund – if you choose to receive dividends
Relevant tax rate would be applicable depending on the source of dividend income. So, let's look at the tax implications of each of the above-mentioned sources of income, separately.
Recent Changes, Updates in Tax on Dividend Income
Up to Assessment Year (AY) 2020-21, if a shareholder received a dividend from a domestic company, s/he was not required to pay any tax on such dividend - because it was exempt from tax under section 10(34) of the Act, subject to Section 115BBDA, which allows for taxability of dividends in excess of Rs 10 lakh. However, under section 115-O, the domestic firm is required to pay Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT).
The DDT was removed by the Finance Act of 2020, and the traditional method of taxation was restored, with dividends taxed in the hands of investors. As a result, regardless of the amount received, dividend income will now be taxable in the hands of taxpayers at the applicable income tax slab rates.
Suggested Read: Income Tax Slabs for AY 2022-23
Tax on Dividend Income
Let us learn about taxation on the dividend income:
- Dividend taxation is determined by whether the dividend receiver is a trader or an investor in securities.
- The income generated by the individual from trading activities is taxable under the heading of “business incomeâ€.As a result, if shares are kept for trading purposes, dividend income is taxable under the heading “income from business or professionâ€.If shares are held as an investment, then the income generated in the form of dividend is taxable under the heading of “ income from other sources â€.
- If the dividend is taxable as business income - the taxpayer can claim tax deduction(s) for all expenses related to earning the dividend income, such as collection fees, interest on a loan, and so on.
- If the dividend is taxed as income from other sources, the taxpayer can claim tax deduction just for the interest expense spent to earn the dividend income of up to 20% of the total dividend income.
- Any additional expenses, such as commission or salary given to a banker or any other person for the purpose of attaining such dividend, are not tax-deductible.
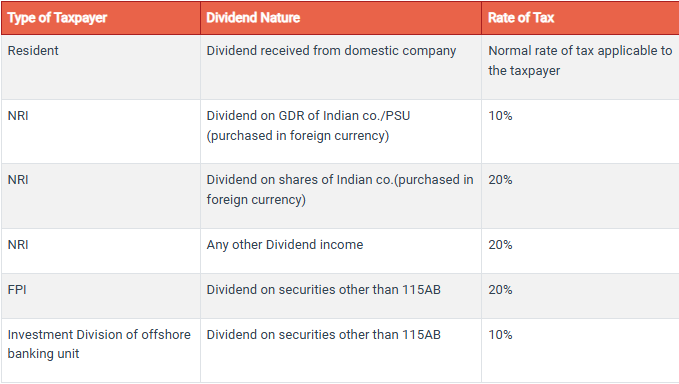
Tax Rates on Dividend Income
Dividend tax rates vary depending on the type of taxpayer receiving the dividend and the instrument used to distribute it.
The following table can help you understand this:
When to Tax Dividend Income?
Here’s when to tax dividend income
- According to the Section 8 of the Act, the final dividends, including deemed dividends, are taxable in the year in which they are declared, distributed, or paid by the company, whichever comes first.
- An interim dividend, on the other hand, is taxable in the year in which the amount of the dividend is unconditionally made available to the shareholder by the firm. In other words, an interim dividend is taxed on the basis of receipt.
TDS on Dividend Income
The TDS on dividend income is charged as follows:
- According to Section 194 , TDS will apply to dividends distributed, declared, or paid on or after April 1, 2020. An Indian company will deduct tax at a rate of 10% from dividends distributed to resident shareholders if the total amount of dividend distributed or paid to a shareholder during the financial year is more Rs. 5,000.
- However, no tax would be deducted from any dividend paid or due to any life insurance company and/or general insurance companies - in respect of any shares in which it owns or has a full beneficial interest.
- When a dividend is paid to a non-resident or a foreign firm, however, the tax is deducted under Section 195 according to the relevant DTAA.
Deduction of Expenses from Dividend Income
The Finance Act of 2020 also allows deduction of interest expense(s) paid against the dividend.
The deduction should not be more than 20% of the dividend income. You cannot claim a deduction for any other expenses paid such as commissions or salary expenses for earning the dividend income.
In the example above, if Mr Ravi borrowed money to invest in equity shares. He paid Rs 2,700 in interest during FY 2021-22. In this case, only Rs 1,200 can be claimed as interest deduction.
Submission of Form 15G/15H
Form 15G can be submitted to the company or mutual fund paying the dividend - by a resident individual - whose projected annual income is below the exemption limit.
In the same way, an elderly citizen with no expected annual tax liability can also file Form 15H to the dividend distributing company.
The corporation or mutual fund notifies shareholders of the dividend declaration via their registered email address and requests that they submit form 15G or form 15H to collect dividend income free of TDS.
Advance Tax and Dividend Income
- If the shortage in the advance tax payment or failure to pay it on time is due to dividend income, no interest will be charged under section 234C if the taxpayer pays the full amount of tax in future advance tax instalments.
- This advantage, however, will not be available in the case of the presumed dividend defined in Section 2(22) (e).
Double Taxation Relief
Even though any dividend received from a foreign firm is taxable in India, it is subject to double taxation if it is also taxable in the country where the foreign company operates.
You can claim double taxation relief in such situations.
You can seek the tax relief under the provisions of the Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) that Indian Government has with other nations' Governments. If an agreement cannot be reached, you can seek relief under Section 91 of the Income Tax Act to avoid paying double tax on the same income.
According to the majority of the DTAAs India has signed with other countries, the dividend is taxed in the source nation in the hands of the beneficial owner of shares at a rate ranging from 5% to 15% of the total amount of the dividends.
The dividend tax rate is further decreased under the DTAA with countries like Canada, Denmark, and Singapore when the dividend is paid to a firm that owns a particular percentage (usually 25%) of shares of the company paying the dividend.
However, there is no minimum time limit in these DTAAs for which the receiving company must keep such a shareholding. As a result, MNCs were frequently detected misusing the laws by raising their stock in the company just before the dividend was declared and selling it after receiving the dividend.
Suggested Read: What is double taxation and how can I prevent it?
Inter-corporate Dividend
The taxability of dividends has transferred from companies to shareholders beginning in AY 2020-21. Hence, Government has added a new Section to the Act – called Section 80M – that prevents the cascading impact when a domestic company gets a dividend from some other domestic company.
Having said that, nothing prevents a domestic company from receiving a dividend from a foreign company and then distributing it to its shareholders. In such cases, the taxable amount is as follows:
- Dividend is paid by one domestic corporation to another domestic company
Section 80M reduces the negative impact – by providing that an intercorporate dividend may be deducted from the total income of the company receiving the dividend, if it is delivered to shareholders one month in advance to the due date for filing the income tax returns .
- Domestic company receives a dividend from a foreign company
Under Section 115BBD, a dividend obtained by a domestic company from a foreign company in which the domestic company owns 26 percent or more equity shares is taxed at a rate of 15 percent plus Surcharge and Health and Education Cess. This tax will be calculated on a gross basis, without any deductions for expenses.
Dividends obtained by a domestic company from a foreign company in which the domestic company's equity shareholding is less than 26% are taxed at the regular tax rate. Any expense made by the domestic company for the purpose of earning such dividend income is deductible.
Suggested Plans
Related Posts
We foster an inclusive workplace where diverse perspectives thrive, and every individual feels valued, respected, and empowered.

Tax Hacks
What are the special income tax benefits for women?

4 mins

18.8K

Posted on: Jul 30, 2025

Tax Hacks
What is the section 10(10D) tax benefit of Generali Central Big Dreams Plan?

2 mins

3.9K

Posted on: Jul 22, 2025

Tax Hacks
Which Generali Central Life Insurance plan can give me section 80C tax benefits?

2 mins

2.9K

Posted on: Jul 22, 2025
Get Expert Advice from Your Trusted Life Insurance Partner!
Have questions? Get help and reliable support from experts at Generali Central India Life Insurance.
Explore Knowledge Centre
From insurance basics to wealth-building strategies — everything you need, in one place.
Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers!
Here are answers to some of the questions you might have.
Life insurance is a financial safety net that supports your loved ones in your absence. If something happens to you, it provides them with funds to help cover everyday expenses, repay debts, and achieve future goals. It gives you peace of mind, knowing your family’s financial future is secure— no matter what.
The right plan depends on your needs.
Start by assessing your life stage, financial goals, and the needs of your family. Consider factors like your income, outstanding loans, future expenses and goals (like children’s education, foreign travel, study abroad), and desired coverage amount. We offer a wide range of plans that cover multiple goals and budgets. To get a better idea and make a confident choice consult with a financial advisor or call us on 1800 102 2355.
A good rule of thumb is to aim for coverage that's 10–15 times your annual income. Consider your family’s living expenses, outstanding loans, children’s education, and long-term goals. The right amount ensures your loved ones can maintain their lifestyle and meet future needs— even in your absence.
We would love to help you choose and buy the right policy for your needs. Call our toll-free number 1800 102 2355 or drop us an email at care@generalicentral.com.
Reach out to us in any way that you prefer, and our team of experts will soon get back to you!
Disclaimers
Understand your policy better with key details and insights into our Generali Central Life Insurance.
This Product is not available for online sale. Life Coverage is included in this Product. For detailed information on this plan including risk factors, exclusions, terms and conditions etc., please refer to the product brochure and consult your advisor, or, visit our website before concluding a sale. Tax benefits are as per the Income Tax Act 1961 and are subject to any amendment made thereto from time to time. If you have any request, grievance, complaint or feedback, you may reach out to us at care@generalicentral.com For further details please access the link: www.generalicentrallife.com/customer-service/grievance-redressal-procedure.
Subscribe to get our best content in your inbox
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated.




