Future Generali India Life Insurance Company Limited is now Generali Central Life Insurance Company Limited. Generali Central Life Insurance Company Limited – A joint venture between Generali – one of the world’s leading insurers and Central Bank of India, India’s finest nationalised bank.
Future Generali India Life Insurance Company Limited is now Generali Central Life Insurance Company Limited. Generali Central Life Insurance Company Limited – A joint venture between Generali – one of the world’s leading insurers and Central Bank of India, India’s finest nationalised bank.
What is Short Term Capital Gains Tax and How It Is Calculated
 13 mins
13 mins 10.2K
10.2KWhat is Short Term Capital Gains Tax?
Gains/profits from the transfer of a short-term capital asset are considered "income" by an individual and are therefore subject to taxation under the India Income Tax Act, 1961.

Capital gains is the profit that an investor enjoys after selling a capital asset.
Capital asset is an umbrella term which includes land, house property, building, gold, equity investments, and various other assets that generate earnings.
Capital Gains are further divided into two categories: Short Term Capital Gain and Long Term Capital Gain.
The division of capital gains into long-term and short-term gains is due to the following reasons:
Capital gains are taxed differently depending on whether they are short-term or long-term. As a result, capital gains must be categorised as short-term or long-term in order to evaluate their taxability. In other words, long-term capital gains and short-term capital gains have different tax rates.
In this article, let us understand short term capital gains in-detail.
What is Short Term Capital Gain?
Short term capital gain refers to any capital gain/profit which an individual gets on the sale of “short term capital assets”.
However, there are a few exceptions to this rule, like gain on depreciable assets is always taxed as short-term capital gain.
For example, Rajesh purchased a flat for Rs 10 lakhs and sold it a year later for 15 lakhs. He earned a profit of Rs 5 lakhs. In this case his short term capital gain is Rs 5 lakh.
What are Short Term Capital Assets?
Short term capital assets are any assets that are owned by a taxpayer for less than or equal to 36 months from the date of initial purchase.
Having said that it is important to note, that the 36-month requirement has been decreased to 12 months for assets such as:
- Equity or preference shares in a company that is listed on a recognised stock exchange of India (listing of shares is not compulsory if the transfer of such shares has taken place on or before July 10, 2014).
- Securities (like bonds, debentures, government securities, and so on) that are listed on a recognized stock exchange in India.
- Units of UTI, whether or not they are quoted.
- Units of equity-oriented mutual funds, regardless of whether they are quoted.
- Bonds with no coupon, whether quoted or not.
It is also important to note that the criteria of 36 months have been reduced to 24 months for assets such as:
- In the case of unlisted company shares or of an immovable property like land, building, or both.
For example, Rajesh purchased a flat on 15 January 2020 and sold it on 12th January 2021, holding it just for a year. Here, Rajesh’s flat will be considered as a short term capital asset.
How is Short-Term Capital Gain Calculated?
The following is how you calculate the short-term capital gain on a transfer of a short-term capital asset:
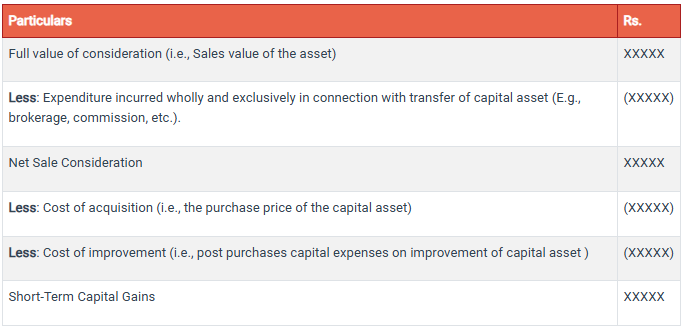
For example:
Mr. Sawant is a salaried employee. In the month of December, 2021 he purchased gold
worth Rs. 8,40,000 and sold the same in August, 2022 for Rs. 9,00,000. At the time of
sale of gold, he paid brokerage of Rs. 10,000.
What is the amount of taxable capital gain?
Gold was purchased in December, 2021 and sold in August, 2022, i.e., sold after holding
it for a period of less than 36 months and, hence, the gain will be short-term capital gain.
The gain will be computed as follows:
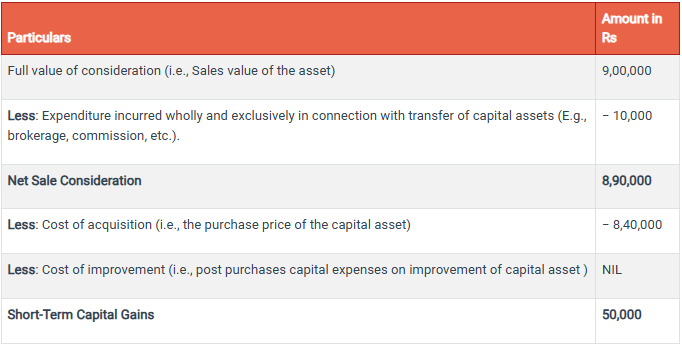
What is Short Term Capital Gains Tax?
Gains/profits from the transfer of a short-term capital asset are considered "income" by an individual and are therefore subject to taxation under the India Income Tax Act, 1961. As a result, any individual who adds the profits from the sale of these assets to their income corpus in the year of asset transfer is subject to taxation on the same amount.
Short-term capital gains are categorised as follows for the purposes of determining the tax rate:
- Short-term capital gains covered under Section 111A.
- Short-term capital gains other than covered under Section 111A.
Examples of STCG Covered under Section 111A
The examples of STCG (Short Term Capital Gains) covered by Section 111A are as follows:
- STCG originating from the sale of equity shares listed on a recognised stock exchange that is chargeable to STT (Securities Transaction Tax).
- STCG is charged to STT when units of equity-oriented mutual funds are sold through a recognised stock exchange.
- STCG deriving from the sale of a business trust's units
- Even if the transaction is not subject to Securities Transaction Tax (STT), STCG may arise on the sale of equity shares, units of an equity oriented mutual fund, or units of a business trust through a recognised stock exchange located in any International Financial Services Centre and consideration is paid or payable in foreign currency.
Example of STCG not covered under Section 111A
The examples of STCG (Short Term Capital Gains) not covered by Section 111A are as follows:
- STCG resulting from the sale of equity shares outside of a recognised stock exchange.
- STCG deriving from the selling of non-equity shares.
- STCG deriving from the selling of units in a debt-oriented mutual fund i.e., non-equity oriented mutual fund).
- Debentures, bonds, and government securities are all subject to the STCG.
- STCG on the sale of assets other than shares/units, such as STCG on sale of immovable items like real estate; along with gold, silver, and other precious metals.
Short Term Capital Gains Tax Rates
STCG subject to Section 111A is taxed at a rate of 15% (plus surcharge and cess as applicable).
Standard STCG, i.e., STCG not covered by Section 111A, is taxed at the normal slab rate, which is calculated based on the taxpayer's total taxable income.
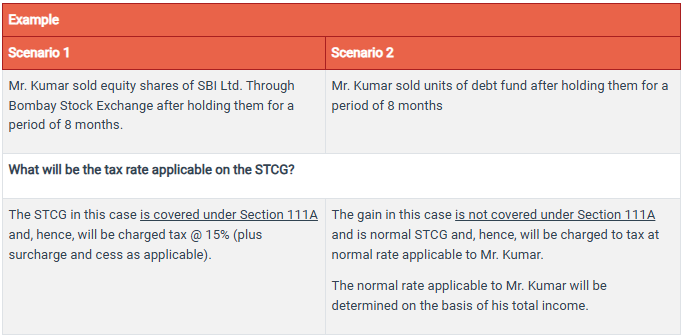
How to Calculate Tax on STCG (Short Term Capital Gains)?
Let us understand how to calculate tax applicable on STCG with the help of the following example:
Mr. Raju Prasad (resident and age 40 years) is a salaried employee working in XYZ Ltd. at an annual salary of Rs. 8,40,000. In December, 2021 he purchased 10,000 equity shares of ABC Ltd. at Rs. 100 per share and sold the same in April, 2022 at Rs. 125 per share (brokerage Re. 1 per share). The shares were sold through Bombay Stock Exchange and securities transaction tax was paid by Mr. Raju Prasad.
What will be the tax liability of Mr. Raju Prasad?
First we have to compute the taxable income of Mr. Raju Prasad and then we will compute the tax liability. The computation of taxable income will be as follows:
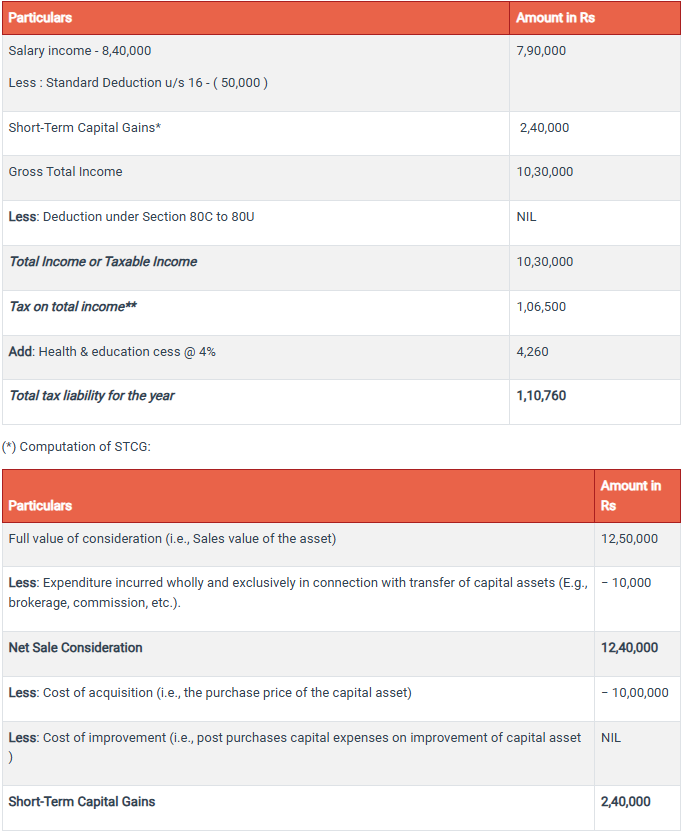
(**)STCG is covered under section 111A and, hence, will be charged to tax @ 15%.
Salaries are considered normal income and are taxed at a normal rate. For the financial year 2021-22, the following are the normal tax rates applicable for the resident individuals under the age of 60:
- Nil up to income of Rs. 2,50,000
- 5% for income above Rs. 2,50,000 but up to Rs. 5,00,000
- 20% for income above Rs. 5,00,000 but up to Rs. 10,00,000
- 30% for income above Rs. 10,00,000.
Apart from the above-mentioned, education and health cess @ 4% will be levied on the taxable amount.
Applying the above normal tax rates, tax on salary income will come to Rs. 70,500 and tax on STCG @ 15% will come to Rs. 36,000 (i.e.15% of Rs. 2,40,000). Total tax will be Rs. 1,06,500. Health and education cess will apply @ 4% on the amount of tax.
Adjustment of STCG against the basic exemption limit
The basic exemption limit is the amount of income above which a person is not required to pay any taxes. For the financial year 2021-22, the basic exemption limit that is applicable in the case of an individual is as follows:
- The exemption limit for residents individuals who are 80 years old or above is Rs 5,00,000.
- The exemption limit for residents individuals who are 60 years old or above but are below 80 years of age is Rs 3,00,000.
- The exemption limit for residents individuals under the age of 60 years is Rs 2,50,000.
- The exemption limit for non-resident individuals, regardless of their age, is Rs 2,50,000.
- The exemption limit for a HUF (Hindu Undivided Family) is Rs 2,50,000.
Please Note:
Only a resident individual or resident HUF (Hindu Undivided Family) has the authority to change the exemption limit for STCG covered under Section 111A.
- As a result, a non-resident individual/HUF cannot increase the exemption limit for STCG covered under Section 111A.
The STCG covered by Section 111A can be adjusted against the basic exemption limit by a resident individual/HUF, but only after other income has been adjusted.
- To put it another way, first income other than STCG covered under Section 111A must be deducted from the exemption limit, and then the leftover limit (if any) must be deducted from STCG covered under Section 111A.
Let us understand this by an example –
Suresh has a taxable salary income of only Rs 1 lakh and a short-term capital gain on the sale of equity shares of Rs 3 lakh. He also has Rs 40,000 as Income from Other Sources. Calculate STCG Tax applicable.
You have to add income from other sources of Rs 40,000 to the total taxable salary thereby making it Rs 1.4 Lakh. As there is a shortfall in the absorption of the basic income tax exemption limit of Ajay by Rs 1.1 lakh, short-term capital gain on the sale of equity can be adjusted to the extent of Rs 1.1 lakh.
Tax will be applicable on a short-term capital gain of Rs.1.9 lakh (Rs 3 lakh –Rs.1.1Lakh) at a flat rate of 15%.
Points to be noted-
- If your total income including STCG after applicable tax deductions is below Rs 2.5 lakhs, then your total tax liability is nil and also no liability will arise us/ 111A as deduction up to the basic tax exemption limit is allowed.
- However, if your total income including STCG is more than Rs 2.5 lakhs, then a flat 15% on STCG will be levied. (However rebate u/s 87a will be available if total income is less than 5 lakhs i.e., up to Rs 12,500 of tax liability as per current income tax regime)
Deductions under Section 80C to 80U and STCG
Short-term capital gains, as defined in Section 111A, are not eligible for a deduction under Sections 80C to 80U. However, other than those covered by Section 111A, such deductions can be claimed from STCG.
Suggested Read: Tax Deductions under Section 80C to 80U
–
Conclusion
Individuals who want to invest in a short term capital asset should be aware of the taxes that will be imposed on their gains. Any loss suffered as a result of the transfer of a short-term capital asset can be set off (adjusted) against any gain realised as a result of the sale or transfer of another short-term capital asset. The most important thing that one must note is that Short term capital loss (STCL) can be set off against both short-term capital gains (STCG) and Long term capital gain (LTCG). Having said that, taxpayers should keep in mind, that this loss cannot be offset against any other income.
Short-term capital losses, on the other hand, can be carried forward for up to eight assessment years from the year during which the losses were occurred.
Suggested Plans
Related Posts
We foster an inclusive workplace where diverse perspectives thrive, and every individual feels valued, respected, and empowered.

Tax Hacks
What are the special income tax benefits for women?

4 mins

18.8K

Posted on: Jul 30, 2025

Tax Hacks
What is the section 10(10D) tax benefit of Generali Central Big Dreams Plan?

2 mins

3.9K

Posted on: Jul 22, 2025

Tax Hacks
Which Generali Central Life Insurance plan can give me section 80C tax benefits?

2 mins

2.9K

Posted on: Jul 22, 2025
Get Expert Advice from Your Trusted Life Insurance Partner!
Have questions? Get help and reliable support from experts at Generali Central India Life Insurance.
Explore Knowledge Centre
From insurance basics to wealth-building strategies — everything you need, in one place.
Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers!
Here are answers to some of the questions you might have.
Life insurance is a financial safety net that supports your loved ones in your absence. If something happens to you, it provides them with funds to help cover everyday expenses, repay debts, and achieve future goals. It gives you peace of mind, knowing your family’s financial future is secure— no matter what.
The right plan depends on your needs.
Start by assessing your life stage, financial goals, and the needs of your family. Consider factors like your income, outstanding loans, future expenses and goals (like children’s education, foreign travel, study abroad), and desired coverage amount. We offer a wide range of plans that cover multiple goals and budgets. To get a better idea and make a confident choice consult with a financial advisor or call us on 1800 102 2355.
A good rule of thumb is to aim for coverage that's 10–15 times your annual income. Consider your family’s living expenses, outstanding loans, children’s education, and long-term goals. The right amount ensures your loved ones can maintain their lifestyle and meet future needs— even in your absence.
We would love to help you choose and buy the right policy for your needs. Call our toll-free number 1800 102 2355 or drop us an email at care@generalicentral.com.
Reach out to us in any way that you prefer, and our team of experts will soon get back to you!
Disclaimers
Understand your policy better with key details and insights into our Generali Central Life Insurance.
This Product is not available for online sale. Life Coverage is included in this Product. For detailed information on this plan including risk factors, exclusions, terms and conditions etc., please refer to the product brochure and consult your advisor, or, visit our website before concluding a sale. Tax benefits are as per the Income Tax Act 1961 and are subject to any amendment made thereto from time to time. If you have any request, grievance, complaint or feedback, you may reach out to us at care@generalicentral.com For further details please access the link: www.generalicentrallife.com/customer-service/grievance-redressal-procedure.
Subscribe to get our best content in your inbox
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated.




