Future Generali India Life Insurance Company Limited is now Generali Central Life Insurance Company Limited. Generali Central Life Insurance Company Limited – A joint venture between Generali – one of the world’s leading insurers and Central Bank of India, India’s finest nationalised bank.
Future Generali India Life Insurance Company Limited is now Generali Central Life Insurance Company Limited. Generali Central Life Insurance Company Limited – A joint venture between Generali – one of the world’s leading insurers and Central Bank of India, India’s finest nationalised bank.

Understanding Income From Salary and How It Is Calculated
 13 mins
13 mins 18.1K
18.1KAccording to the Section 14 of the Income Tax Act of 1961, there are five main income tax heads for a person. Income tax calculation is a crucial step that must be done in accordance with an individual's income. The income must be correctly classified in order to avoid any confusion throughout the calculating process. Hence, first let us understand the five income tax heads.
The five main income tax heads are as follows:
- Income from Salary
- Income from House Property
- Income from Profits and Gains of Profession or Business
- Income from Capital Gains
- Income from Other Sources
Out of these five heads, in this article we will focus only on the first head i.e., Income from Salary.
What is Income from Salary?
The income or payment that a person receives in exchange for providing services or signing contracts is known as "income from salary". This section simply incorporates the compensation that an individual receives for the services that he provides under the employment contract.
However, it is important to note that the payment received by the person will be regarded as income for the purpose of the Income Tax Act only if – there is an "employer-employee relationship" between the parties providing the payment and the party receiving it.
What is employer and employee relationship?
If there is an employer-employee relationship between the payer and the receiver, any payment received by the employee (the receiver) will be regarded as income under the Income Tax Act. Both must be in a master-servant relationship in order for income to be considered to be earned on a salary. Where a servant is someone who is responsible for carrying out the work in the manner instructed by his master (employer), a master is someone who guides his servant (employee) as to what has to be done and how it should be done.
Meaning of Salary
The salary for the purpose of calculation of income from salary includes:
- Wages;
- Pension;
- Annuity;
- Gratuity;
- Advance Salary paid;
- Fees, Commission, Perquisites, Profits in lieu of or in addition to Salary or Wages;
- Annual accretion to the balance of Recognized Provident Fund;
- Leave Encashment ;
- Transferred balance in Recognized Provident Fund;
- Contribution by Central Govt. or any other employer to Employees Pension A/c as referred in Sec. 80CCD .
What is CTC?
One of the vague words used to describe salaries is CTC. Cost To Company is referred to as CTC. It is the sum that the organization will spend on bringing on and keeping an employee.
CTC covers an employee's income as well as any other perks they receive, such as meal vouchers, office space rent, Provident Fund contributions, medical insurance, House Rent Allowances (HRA) , and any other expenses incurred by the firm.
It should be remembered that CTC contains variables more than the actual salary that a person is receiving, hence CTC differs from the actual income from salary that a person receives.
Components of Income from Salary

CTC vs Take Home Salary
Up until this point, we have learnt about the elements of your salary that make up your CTC. However, your pay is not equal to your CTC when you receive it at the end of the month. What happens, then?
Your CTC, for instance, is Rs 12,00,000. You won't get just Rs 1,00,000 per month (Rs 12,00,000 divided by 12 months). This is due to the fact that your CTC is subject to various deductions. Your employer's deductions for taxes and exemptions account for the difference between your take-home pay and CTC.
Hence, your take home salary will be:
- Gross Cost To Company CTC
- Minus- Medical Insurance, Reimbursement of food coupons, other perquisites, contribution to provident fund, Professional Tax and so on.
- Minus- Net tax payable by the employee. Net tax liability is calculated by deducting the deduction under Chapter VIA ( Section 80C , Section 80D , Section 80DDB , etc.) and applying the tax slab.
Taxability of Components of Salary
We now know what goes into salaries and what determines your take-home pay. To assist you in planning your taxes, let's now examine the taxability of each salary component.
- Taxability of Salary Income

- Tax on Allowances
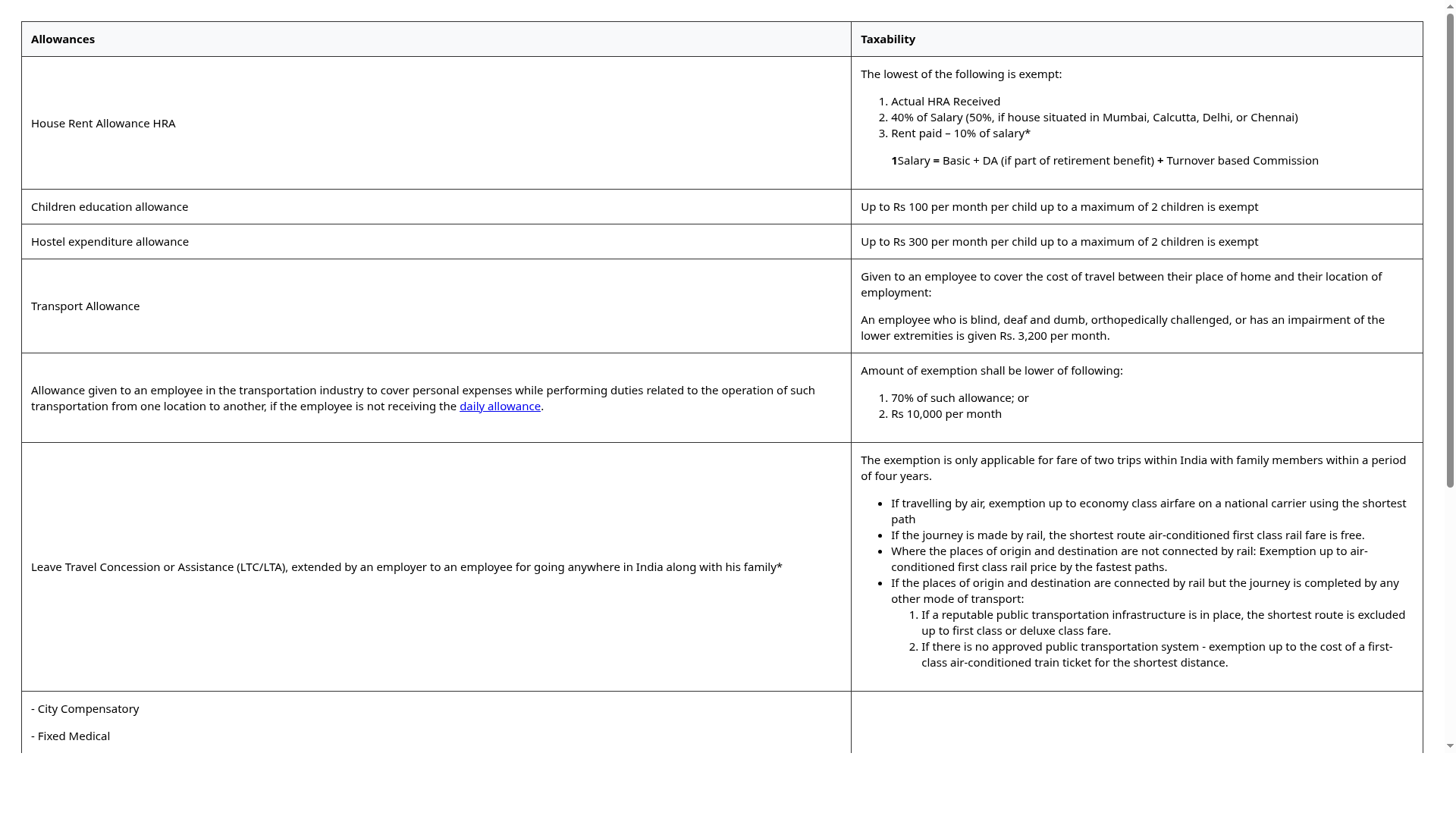
- Tax on Perquisites
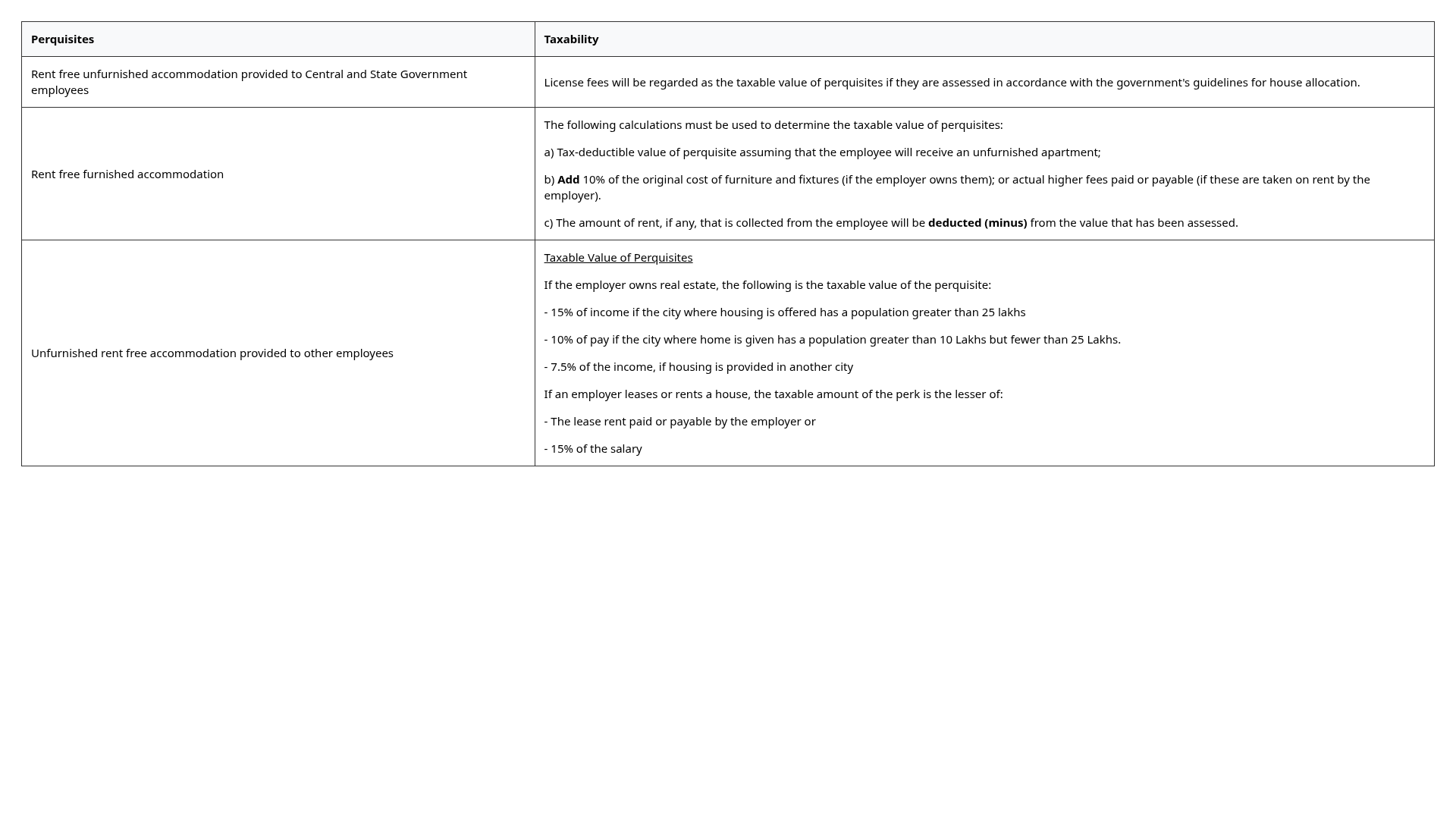
How to Calculate Taxable Income from Salary?
Gather all the documentation relevant to salary income first. Your monthly pay-slips, Form 16 Parts A and B, and Form 26AS are required here.

Suggested Read: How to Calculate Income Tax on Salary with Example
Tax Relief and Tax Rebate
Tax Rebate – You may be eligible for a tax rebate (refund) of up to Rs12,500 if your total taxable income is up to Rs 5,00,000. After taking into account all applicable deductions, exemptions, and allowances, the total taxable income is determined. Both the old and new tax regimes allow for tax rebate. However,Union Budget 2023 has proposed that if the Assessee has opted for New Regime then he/she is eligible for a tax rebate (refund) of up to Rs 25,000 if your total taxable income is up to Rs 7,00,000. The same is applicable from Financial Year 2023-24 i.e Assessment Year 2024-25.
Tax Relief – If you received any salary delays during the fiscal year, you may be eligible for tax relief under Section 89.
Standard Deduction
The exemption from refund for travel expenses and medical expenses has been replaced by the standard deduction. The exemptions have been combined. Beginning with the 2019–20 fiscal year, you are eligible to deduct up to Rs 50,000 from your travel and medical expenses. No receipts or other written documentation supporting the costs must be provided. However, the new tax system does not allow for standard deductions.
If your only source of income for the entire fiscal year is a salary, you can use the aforementioned method. You might also make money from other sources, such as rental income, business or professional income, or income from capital gains. In this scenario, you must add the income from all of these sources before calculating the net tax due.
Important Documents to File Tax on Income From Salary
The following are the some of the important documents to file tax on income from salary:
- Form 16At the end of the financial year, an employer gives Form 16 to its employees. For the purpose of calculating taxes that are due and taxes that are refundable, Form 16 includes information on gross salary, deductions, exemptions, and TDS . In addition, every taxpayer is required by the Income Tax Act of 1961 to submit Form 16 prior to the deadline.There are two parts of Form 16, such as follows:Your employer's information, including TAN, PAN, address, and firm name, is contained in Form 16 Part-A.The information on salary, deductions, and net tax payable is contained in Form 16 Part-B.As you are completing and submitting your income tax return, you must make use of your Form 16.
- Form 26ASA tax credit statement called Form 26AS lists the TDS that your employer and other taxpayer have deducted from your pay. It also includes information on any advance taxes or self-assessment taxes you may have paid. To confirm that your employer is truly deducting and paying the TDS deducted to the account (credit) of the Central Government, you must refer to Form 26AS. You will not be eligible to claim the TDS refund until and unless your employer is paying the TDS deducted to the credit of the Central Government.
- Capital Gain StatementYour investments in ULIPs, mutual funds, company shares, stocks, etc. would have generated returns for you. When you sell multiple units of mutual funds or shares, it is frequently challenging to determine the capital gain. In this situation, it is preferable to ask the asset management company for mutual funds or the broker for shares for a capital gain statement. You can simply determine the overall capital gains for tax purposes in this method.
- Income Tax Return ITREvery taxpayer who has taxable income that is greater than the standard exemption amount is required to file an income tax return. The kind of taxpayer and the categories of income earned during the financial year determine whether the ITR is applicable.
Suggested Plans
Related Posts
We foster an inclusive workplace where diverse perspectives thrive, and every individual feels valued, respected, and empowered.

Tax Hacks
What are the special income tax benefits for women?

4 mins

18.8K

Posted on: Jul 30, 2025

Tax Hacks
What is the section 10(10D) tax benefit of Generali Central Big Dreams Plan?

2 mins

3.9K

Posted on: Jul 22, 2025

Tax Hacks
Which Generali Central Life Insurance plan can give me section 80C tax benefits?

2 mins

2.9K

Posted on: Jul 22, 2025
Get Expert Advice from Your Trusted Life Insurance Partner!
Have questions? Get help and reliable support from experts at Generali Central India Life Insurance.
Explore Knowledge Centre
From insurance basics to wealth-building strategies — everything you need, in one place.
Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers!
Here are answers to some of the questions you might have.
Life insurance is a financial safety net that supports your loved ones in your absence. If something happens to you, it provides them with funds to help cover everyday expenses, repay debts, and achieve future goals. It gives you peace of mind, knowing your family’s financial future is secure— no matter what.
The right plan depends on your needs.
Start by assessing your life stage, financial goals, and the needs of your family. Consider factors like your income, outstanding loans, future expenses and goals (like children’s education, foreign travel, study abroad), and desired coverage amount. We offer a wide range of plans that cover multiple goals and budgets. To get a better idea and make a confident choice consult with a financial advisor or call us on 1800 102 2355.
A good rule of thumb is to aim for coverage that's 10–15 times your annual income. Consider your family’s living expenses, outstanding loans, children’s education, and long-term goals. The right amount ensures your loved ones can maintain their lifestyle and meet future needs— even in your absence.
We would love to help you choose and buy the right policy for your needs. Call our toll-free number 1800 102 2355 or drop us an email at care@generalicentral.com.
Reach out to us in any way that you prefer, and our team of experts will soon get back to you!
Disclaimers
Understand your policy better with key details and insights into our Generali Central Life Insurance.
This Product is not available for online sale. Life Coverage is included in this Product. For detailed information on this plan including risk factors, exclusions, terms and conditions etc., please refer to the product brochure and consult your advisor, or, visit our website before concluding a sale. Tax benefits are as per the Income Tax Act 1961 and are subject to any amendment made thereto from time to time. If you have any request, grievance, complaint or feedback, you may reach out to us at care@generalicentral.com For further details please access the link: www.generalicentrallife.com/customer-service/grievance-redressal-procedure.
Subscribe to get our best content in your inbox
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated.




